Amortizing Bond Premium Using the Effective Interest Rate Method

To illustrate the premium on bonds payable, let’s assume that in early December 2022, a corporation has prepared a $100,000 bond with a stated interest rate of 9% per annum (9% per year). The bond is dated as of January 1, 2023 and has a maturity date of December 31, 2027. The bond’s interest payment dates are June 30 and December 31 of each year.
The amount received for the bond (excluding accrued interest) that is in excess of the bond’s face amount is known as the premium on bonds payable, bond premium, or premium. As before, the final bond accounting journal would be to repay the face value of the bond with cash. Notice that the effect of this journal is to post the interest calculated in the bond amortization schedule (5,338) to the interest expense account. From the bond amortization schedule, we can see that at the end of period 4, the ending book value of the bond is reduced to 120,000, and the premium on bonds payable (2,204) has been amortized to interest expense. The final bond accounting journal would be to repay the par value of the bond with cash. The straight line amortization method is one method of calculating how the premium or discount on bonds payable should be amortized to the interest expense account over the lifetime of the bond.
Amortizing Bond Premium with the Effective Interest Rate Method
Under the straight-line method the interest expense remains at a constant amount even though the book value of the bond is increasing. The accounting profession prefers the effective interest rate method, but allows the straight-line method when the amount of bond discount is not significant. For the remaining eight periods (there are 10 accrual or payment periods for a semi-annual bond with a maturity of five years), use the same structure presented above to calculate the amortizable bond premium.
- Lighting Process, Inc. issues $10,000 ten‐year bonds, with a coupon interest rate of 9% and semiannual interest payments payable on June 30 and Dec. 31, issued on July 1 when the market interest rate is 10%.
- Study the following illustration, and observe that the Premium on Bonds Payable is established at $8,530, then reduced by $853 every interest date, bringing the final balance to zero at maturity.
- Notice that interest expense is the same each year, even though the net book value of the bond (bond plus remaining premium) is declining each year due to amortization.
- Don’t be put off by the work involved in the effective interest method.
- Usually, when the bond’s actual interest rates are higher than the market, it will become a premium bond.
An unamortized bond premium refers to the difference between a bond’s face value and its sale price. If a bond is sold at a discount, for instance, at 90 cents on the dollar, the issuer must still repay the full 100 cents of face value at par. Since this interest amount has not yet been paid to bondholders, it is a liability for the issuer. The premium account balance represents the difference (excess) between the cash received and the principal amount of the bonds. The premium account balance of $1,246 is amortized against interest expense over the twenty interest periods. Unlike the discount that results in additional interest expense when it is amortized, the amortization of premium decreases interest expense.
What is Premium on Bonds Payable?
As mentioned, the difference between the bond and market coupon rate can reveal that information. Since we’re assuming a six-month accrual period, the yield and coupon rate will be divided by 2. The interest expense is amortized over the twenty periods during which interest is paid. Amortization of the discount may be done using the straight‐line or the effective interest method.
When an issuer charges a lower price for their bond, it falls under a bond discount. Usually, this party includes a financial institution that acts as an intermediary. This institution facilitates the process between the bond issuer and the holder. Thus, interest expense is recorded how to calculate premium on bonds payable as $4,324.44 for the first period, while $675.56 is recorded as premium amortization. The actual cash interest paid was only $5, the coupon multiplied by the bond’s face value. However, interest expense also includes the $558.39 of amortized discount in the first six months.
What is premium on bonds payable?
The accounting profession prefers the effective interest rate method, but allows the straight-line method when the amount of bond premium is not significant. Over the life of the bond, the balance in the account Premium on Bonds Payable must be reduced to $0. In our example, the bond premium of $4,100 must be reduced to $0 during the bond’s 5-year life. By reducing the bond premium to $0, the bond’s book value will be decreasing from $104,100 on January 1, 2023 to $100,000 when the bonds mature on December 31, 2027.
The purpose of the amortisation is to provide a better reflection of the borrowing costs incurred by ABC for this debt funding. Because of the cash received compared to the liability taken on, the premium, difference between the market rate and the coupon rate, in affect off-sets the interest being paid at the higher rate of 7 per cent. Assume that a corporation prepares to issue bonds having a maturity value of $10,000,000 and a stated interest rate of 6%.
The total present value of the payments from the bond will be as follows. Bond investors need to know how to deal with bonds that cost more than their face value. Intrinsically, a bond purchased at a premium has a negative accrual; in other words, the basis amortizes. Investing in stocks and bonds can help to build wealth for anyone with disposable income. The following T-account shows how the balance in Discount on Bonds Payable will be decreasing over the 5-year life of the bond. We’ll come back to these net interest expense figures once we have looked at the effective interest method – this will highlight the differences the two methods produce.
Top Slicing Relief for Bonds Taxation M&G Wealth Adviser – M&G plc
Top Slicing Relief for Bonds Taxation M&G Wealth Adviser.
Posted: Fri, 09 Feb 2024 21:25:17 GMT [source]
How to Invoice as a Freelancer: 2023 Guide

The former Trump allies are each expected to take a turn on the witness stand, giving testimony that could help make him the first president convicted of a felony. Over the past five trial days, the judge overseeing the case, Juan M. Merchan, has shown that he is eager to keep this trial on schedule. He seems serious about keeping his word to the jurors that the trial will last six weeks. Prosecutors’ first witness was David Pecker, the longtime publisher of The National Enquirer.

Make sure to send payment reminders through your accounting software just before the due date if it hasn’t been paid. Sending out invoices is how you get paid for your freelance work. I know the term says “free” right in it, but that’s an indication of your employment status, not your lack of payment. This is the official document you send to a client that ensures you get paid the proper amount for the services you provided, without sending them the money probably won’t end up in your bank account.
What should a freelance invoice look like?
There are also some free options, such as AND CO and Invoicely, which may meet many freelancers’ needs. Invoicing is often a feature of more robust accounting and/or payroll systems. For example, Lam has stuck with QuickBooks Self-Employed because she also uses it to track her business expenses.

Close to 60% are owed $50,000 or more for already completed work. The reality is that your clients aren’t likely to pay you right away. That means, if paying you takes time and energy, they might put it aside for a few days—or weeks.
How to Move from Another Payment Management System to Finli
She has a journalistic approach to writing, providing audiences with educational and informative insights for their careers. From self-guided resources to expert help from real people, you can count on dependable support services that are always there for you. You can do the creative how to invoice as a freelancer work…but can you promote your services, then get someone to pay you for them? Beyond all the different items above, there are a few other things you can add to your invoice if it makes sense for you. Include a short description of work that your client will recognize.
As a freelancer, you might have to answer client questions about your work or track down late payment. Having organized records of invoices will help you answer those questions when they come up. An invoice number will help the client and you know that you are talking about the same transaction. When you’re working as a freelancer, it is up to you to get paid for the work you have done for your clients. You might have provided your client a quote that let your client know how much their job request from you would cost. An invoice is provided after your work is completed to explain the work that has been done and the amount of money you expect to be paid for the work you have completed.
Create an Invoice Yourself
In short, these are important documents your business needs to get right. So, whether you have a freelance side hustle or are building a six-figure freelance career, know that the little details matter. No matter what method you use, your invoice should have the right information to help you get paid. Invoices are also used for audits, financial tracking and analysis, and tax preparation. Using software is probably the fastest and most efficient way to make an invoice for freelance work. They’re also easier to manage because you can store them digitally.
- If you charge by the hour, specify your hourly rate and the number of hours worked, providing a detailed breakdown of the hours and the corresponding charges.
- If you’re sending a digital invoice with invoicing software, you can give them the option to pay you electronically.
- If you need a faster payment, all you have to do is clearly specify that on the invoice.
- As 1Password is offered by a Canadian company, American and European customers may receive a foreign transaction charge when paying with non-Canadian bank accounts or credit cards.
- It also helps eliminate any confusion or misunderstanding between the freelancer and the client.
What Are Accruals?
This account is a liability because the company has an obligation to deliver the good or provide the service in the future. Accrual accounting is helpful because it shows underlying business transactions, not just those with cash involved. Most transactions a company has are straightforward, with payment happening at the time of the transaction.
For a large company, the general ledger will be flooded with transactions that report items that have had no bearing on the company’s bank statement nor impact to the current amount of cash on hand. The accrual of revenues and assets refers to revenues and/or assets that a company has earned, but the company has not yet received the money nor has it recorded the transaction. The accrual of revenues will usually involve an accrual adjusting entry that increases a company’s revenues and increases its current assets. Understanding how accrual accounting works is essential for any business looking to manage its finances effectively. Moreover, using accruals enhances transparency and credibility in financial reporting. Stakeholders such as investors, lenders, and suppliers rely on accurate financial information to assess a company’s creditworthiness and make investment decisions.
All applicants must be at least 18 years of age, proficient in English, and committed to learning and engaging with fellow participants throughout the program. The applications vary slightly from program to program, but all ask for some personal background information. If you are new to HBS Online, you will be required to set up an account before starting an application for the program of your choice. No, all of our programs are 100 percent online, and available to participants regardless of their location. Harvard Business School Online’s Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- The accrual method of accounting is based on the matching principle, which states that all revenue and expenses must be reported in the same period and “matched” to determine profits and losses for the period.
- You should always create accrual journal entries so that they automatically reverse themselves in the next accounting period.
- This can be made a lot easier by using the double-entry bookkeeping system and by keeping your records as detailed as possible.
- Accrual accounting often involves adjusting entries and complex calculations, which can make financial reports more difficult to understand for stakeholders who are not familiar with this method.
- To add to the confusion, some legalistic accounting systems take a simplistic view of accrued revenue and accrued expenses, defining each as revenue or expense that has not been formally invoiced.
Unfortunately, cash transactions don’t give information about other important business activities, such as revenue based on credit extended to customers or a company’s future liabilities. By recording accruals, a company can measure what it owes in the short-term and also what cash revenue it expects to receive. It also allows a company to record assets that do not have a cash value, such as goodwill. Both accrual and accounts payable are accounting entries that appear on a company’s financial statements.
Definition of Accruals
When the AP department receives the invoice, it records a $500 credit in the accounts payable field and a $500 debit to office supply expense. As a result, if anyone looks at the balance in the accounts payable category, they will see the total amount the business owes all of its vendors and short-term lenders. The company then writes a check to pay the bill, so the accountant enters a $500 credit to the checking account and enters a debit for $500 in the accounts payable column. Deferred revenue typically occurs when a company receives an advance payment for a service that will be provided in the future.
- Accrued revenue situations may last for several accounting periods, until the appropriate time to invoice the customer.
- Some accrual policies have the ability to carry over or roll over some or all unused time that has been accrued into the next year.
- Persons interested in practicing a regulated profession must contact the appropriate state regulatory agency for their field of interest.
- This includes invoices, receipts, and any other documents that pertain to expenses or revenue.
- Accrual accounting matches revenue and expenses to the current accounting period so that everything is even.
In accrual-based accounting, revenue is recognized when it is earned, regardless of when the payment is received. Similarly, expenses are recorded when they are incurred, regardless of when they are paid. For example, if a company incurs expenses in December for a service that will be received in January, the expenses would be recorded in December, when they were incurred. For example, if a company has performed a service for a customer, but has not yet received payment, the revenue from that service would be recorded as an accrual in the company’s financial statements.
Why are accruals used?
This principle states that revenues and expenses should be recognized in the financial statements that correspond to when they are earned, regardless of when payment is received. In other words, accrual accounting focuses on the timing of the work that a business does to earn revenue, rather than focusing on the timing of payment. While accrual accounting is the most widely used accounting method, some businesses prefer to use cash basis accounting. Cash accounting is an accounting method in which revenue is only recorded when cash is received, and expenses are recorded after cash payments are made. If an accrual is recorded for an expense, you are debiting the expense account and crediting an accrued liability account (which appears in the balance sheet). Therefore, when you accrue an expense, it appears in the current liabilities portion of the balance sheet.
Prepaid expenses are payments made in advance for goods and services that are expected to be provided or used in the future. While accrued expenses represent liabilities, prepaid expenses are recognized as assets on the balance sheet. This is because the company is expected to receive future economic benefit from the prepayment. Additionally, because accrual accounting records revenue and expenses when they are earned or incurred rather than when cash actually changes hands, it may not accurately reflect a company’s cash flow situation. This can lead to discrepancies between reported profits and actual available funds.
Accrual Accounting vs. Cash Basis Accounting Example
Accrual accounts include, among many others, accounts payable, accounts receivable, accrued tax liabilities, and accrued interest earned or payable. On the other hand, an accrued expense is an event that has already occurred in which cash has not been a factor. Not only has the company already received the benefit, it still needs to remit payment. Therefore, it is literally the opposite of a prepayment; an accrual is the recognition of something that has already happened in which cash is yet to be settled.
Likewise, expenses for goods and services are recorded before any cash is paid out for them. This follows the accrual accounting principle, which states that revenue should be recognized when earned, regardless of when payment is received. There are a handful of generally accepted accounting principles that govern how revenue is accounted for in different scenarios and that are important for businesses to adhere to.
The unbilled revenue account should appear in the current assets portion of the balance sheet. Thus, the offsets to accruals in the income statement can appear as either assets or liabilities in the balance sheet. Company X has insured one of its buildings and gets billed for this service twice a year ($500 each time). Accruals are expenses or revenues incurred in a period for which no invoice was sent or no money changed hands. If for example, you’re in an ongoing court case, you can assume that legal fees will need to be paid in the near future and not straightaway so you have to factor that into your calculations.
Best Online Bookkeeping Services
This ensures that the company’s financial statements accurately reflect its true financial position, even if it has not yet received payment for all of the services it has provided. To create an effective accruals balance sheet for your business, start by recording transactions based on the matching principle – recognizing revenues when earned and expenses when incurred. Be diligent in tracking accounts receivable/payable as well as any outstanding invoices or bills. Businesses use accruals to accurately report revenue and expenses that have been earned or incurred but not yet received or paid for. It allows for better matching of income and expenses over time while maintaining compliance with accounting standards. By understanding how to properly utilize accruals, companies can make informed decisions based on reliable financial information.
Also called accrued liabilities, these expenses are realized on a company’s balance sheet and are usually current liabilities. Accrued liabilities are adjusted and recognized on the balance sheet at the end of each accounting period. Any adjustments that are required are used to document goods and services that have been delivered but not yet billed. Because accrued revenue can have a significant impact on a business’s financial statements, it’s important to track and record it accurately.
Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem. It’s beneficial to sole proprietorships and small businesses because, most likely, it won’t require added staff (and related expenses) to use. In payroll, a common benefit that an employer will provide for employees is a vacation or sick accrual. This means that as time passes, an employee accumulates additional sick leave or vacation time and this time is placed into a bank.
Accrual Accounting vs. Cash Basis Accounting: An Overview
The expected cost of internet for the month will need to be recorded as an accrued expense at the end of January. Accrued expenses, also known as accrued liabilities, occur when a company incurs an expense it hasn’t yet been billed for. Essentially, net positive the company received a good or service that it will pay for in the future. For example, imagine a dental office buys a year-long magazine subscription for $144 ($12 per month) so patients have something to read while they wait for appointments.
Wholesale and Distribution Accounting
The cost of an accounting software for distribution companies will depend on many factors, including the size of the company, the number of users, and any additional features or modules needed. Generally speaking, accounting software for distribution businesses can range in cost from a few hundred to a few thousand dollars. The features of accounting software for distribution businesses vary depending on the specific product.
Owner’s distributions are earnings an owner withdraws from their business. Here note that distribution expenses are different from selling and marketing expenses. It is mainly concern with logistics, shipping, and insurance while the selling and marketing expenses are mainly concern with the advertisement, commission, https://www.bookstime.com/ and salaries of marketing staff. We continue to engage with relationships in the distribution industry on Product Portfolio Analysis as part of our Distribution Accounting practice. In fact, we have designed an Excel tool that assists our relationships in developing product strategy on their existing business.
Manufacturers selling direct.
With the increase in completion in every industry, manufacturers and distributors want to cut down their expenses to meet the cut-throat price war in the market. Gravity Software is designed especially for multi-entity companies that have outgrown their entry-level accounting software, including wholesale distribution companies. QuickBooks is a comprehensive accounting software for small to medium-sized businesses.

We also offers bookkeeping services to accounting for distribution companies and wholesale distributors. When accounting for wholesale distribution receives a purchase order, it will remove the merchandise from its warehouse and distribute it to a customer. When it comes to estimating the cost of products sold, the corporation has a few possibilities. Distribution companies buy goods and resell them for a profit, usually from business to business.
Wholesale Distribution Challenges
It is aimed at businesses of all sizes and includes integrations with various other business tools. NetSuite is a cloud-based accounting software that provides financial management, inventory management, and order management features. accounting for distribution companies Zoho Books is a cloud-based accounting software that provides features such as invoicing, expense tracking, and inventory management. It is aimed at small businesses and includes integrations with various other business tools.
Aprio Admits Joseph Ventura INSIDEPublicAccounting – INSIDE Public Accounting
Aprio Admits Joseph Ventura INSIDEPublicAccounting.
Posted: Mon, 13 Nov 2023 16:41:40 GMT [source]
Answered: Under the allowance method, if a
That journal entry assumed a zero balance in Allowance for Doubtful Accounts from the prior period. This journal entry takes into account a debit balance of $20,000 and adds the prior period’s balance to the estimated balance of $58,097 in the current period. The journal entry for the Bad Debt Expense increases (debit) the expense’s balance, and the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts increases (credit) the balance in the Allowance. The allowance for doubtful accounts is a contra asset account and is subtracted from Accounts Receivable to determine the Net Realizable Value of the Accounts Receivable account on the balance sheet. In the case of the allowance for doubtful accounts, it is a contra account that is used to reduce the Controlling account, Accounts Receivable. The allowance method is the more widely used method because it satisfies the matching principle.
Although, the number of days passed since invoice overdue is an essential factor in determining if a specific balance should be written down. However, several other factors like the reputation of the customer, past trends, and business relations with them must be assessed. At the end of an accounting period, the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts reduces the Accounts Receivable to produce Net Accounts Receivable. Note that allowance for doubtful accounts reduces the overall accounts receivable account, not a specific accounts receivable assigned to a customer. Because it is an estimation, it means the exact account that is (or will become) uncollectible is not yet known. Using this allowance method, the estimated balance required for the allowance for doubtful accounts at the end of the accounting period is 7,100.
- The percentage of credit sales approach focuses on the income statement and the matching principle.
- Using the allowance method, complying with the matching principle, the amount is recorded in the current accounting period with the following percentage of credit sales method journal.
- The longer the time passes with a receivable unpaid, the lower the probability that it will get collected.
- Further, allowance for doubtful accounts is debited when the debtor balance is identified as written off.
- The credit side leads to eliminating the account balance not expected to be collected from customers.
- The Bad Debts Expense remains at $10,000; it is not directly affected by the journal entry write-off.
In addition, from an audit perspective, the default risk of debtors is an overstatement. The creation of the allowance helps to bring an element of fairness to the financial statement as the net balance is shown after deducting the provision. The net impact of these two entries is receipt of the cash and elimination of the debtor’s balance in the books; the treatment is the same as a normal cash receipt. Since we had $2,000 in the opening and the required estimate for the allowance was $12,000. Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI’s full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
In order to use the allowance method, it is first necessary to estimate the allowance needed using a suitable method. The entry has reinstated the customer balance, and now we need to record the cash receipt. It’s important to note that we have assumed the opening allowance for the bad debt as zero in the above entry. Bad Debt Expense increases (debit) as does Allowance for Doubtful Accounts (credit) for $58,097. On the other hand, writing off through the allowance method helps to locate the creation of provision, use of the provision, reversal, etc. From a control perspective, the use of the direct method can be a little risky, it’s because if there are no sound controls manager might write off balances in a personal capacity.
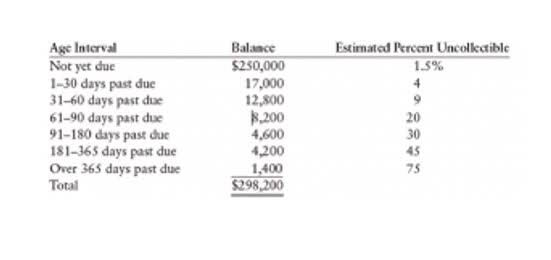
Aging of Accounts Receivable Method Example
The allowance method estimates bad debt during a period, based on certain computational approaches. When the estimation is recorded at the end of a period, the following entry occurs. The final point relates to companies with very little exposure to the possibility of bad debts, typically, entities that rarely offer credit to its customers.
However, there is a difference between allowance creation and a direct write-off. Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Double Entry Bookkeeping. He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries. He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own. He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University.
This is because it considers the amount of time that accounts receivable has been owed, and it assumes that the longer the time owed, the greater the possibility that individual accounts receivable will prove to be uncollectible. The percentage of receivables method estimates the allowance for doubtful accounts using a percentage of the accounts receivable at the end of the accounting period. As the accountant for a large publicly traded food company, you are considering whether or not you need to change your bad debt estimation method. You currently use the income statement method to estimate bad debt at 4.5% of credit sales.
Free Financial Statements Cheat Sheet
So, the allowance method allows organizations to create a general reserve for bad debt that can be used when the business needs to write off specific balances. The bad debt expense is then the difference between the calculated allowance for doubtful accounts at the end of the account period and the current allowance for doubtful accounts before adjustment. The historical bad debt experience of a company has been 3% of sales, and the current month’s sales are $1,000,000. Based on this information, the bad debt reserve to be set aside is $30,000 (calculated as $1,000,000 x 3%). In the following month, $20,000 of the accounts receivable are written off, leaving $10,000 of the reserve still available for additional write-offs.
Balance Sheet
However, at some later date, the balance in the allowance account must be reviewed and perhaps further adjusted, so that the balance sheet will report the correct net realizable value. If the seller is a new company, it might calculate its bad debts expense by using an industry average until it develops its own experience rate. The balance sheet method (also known as the percentage of accounts receivable method) estimates bad debt expenses based on the balance in accounts receivable. The method looks at the balance of accounts receivable at the end of the period and assumes that a certain amount will not be collected. Accounts receivable is reported on the balance sheet; thus, it is called the balance sheet method. The balance sheet method is another simple method for calculating bad debt, but it too does not consider how long a debt has been outstanding and the role that plays in debt recovery.
As you’ve learned, the delayed recognition of bad debt violates GAAP, specifically the matching principle. Therefore, the direct write-off method is not used for publicly traded company reporting; the allowance method is used instead. Whenever there is bad debt, there is a reserve account for all these bad debts as the organizations use accrual methods to record the transactions. When the organization’s financial statements are finalized, these expenses are reviewed by the higher management to understand the financial reporting process better and control the business’s credit aspects.
Record a journal entry for providing an allowance
Further, the creation of the reserve is based on the balance of receivables or the percentage of sales generated by the organization during a specific reporting period under consideration. The process is also encouraged by the prudence concept of accounting, as bad debt expense is recorded before the actual write-off. Sometimes the business has already written off a certain amount, and an unexpected receipt is made from the customer. In this scenario, we need to reverse the allowance for receivables and reinstate the account balance. The accounts receivable method for the allowance calculation is more sophisticated and uses the aging report to assess the amount for the allowance.
On August 24, that same customer informs Gem Merchandise Co. that it has filed for bankruptcy. It also states that the liquidation value of those assets is less than the amount it owes the bank, and as a result Gem will receive nothing toward its $1,400 accounts receivable. After confirming this information, Gem concludes that it should remove, or write off, the customer’s account balance of $1,400.
How to estimate the allowance for bad debts?
You are considering switching to the balance sheet aging of receivables method. This would split accounts receivable into three past- due categories and assign a percentage to each group. Net realizable value is the amount the company expects to collect from accounts receivable. When the firm makes the bad debts adjusting entry, it does not know which specific accounts will become uncollectible. Thus, the company cannot enter credits in either the Accounts Receivable control account or the customers’ accounts receivable subsidiary ledger accounts. If only one or the other were credited, the Accounts Receivable control account balance would not agree with the total of the balances in the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger.
Then, in the next accounting period, a lot of their customers could default on their payments (not pay them), thus making the company experience a decline in its net income. Therefore, what is a forward contract the direct write-off method can only be appropriate for small immaterial amounts. We will demonstrate how to record the journal entries of bad debt using MS Excel.
For instance, the company may have a policy to (Based on past trends) provide 30% on balance overdue from days and 50% on balance due 90 plus days. The two methods used in estimating bad debt expense are 1) Percentage of sales and 2) Percentage of receivables. The debit impact of this journal entry is the same as in the case of the indirect method. However, credit entry eliminates the debtor’s balance from the books without taking away allowance creation. In contrast, the credit side of the journal entry creates a contra account to adjust the overstated debtor in the form of uncollectible assets. Over time since an invoice was written off, a customer may unexpectedly pay an invoice.

Villa akció – golfozó gyerekeknek
Akciós ajánlatunk golfozó gyerekeknek 18 éves korig: Green fee napi ár 50% kedvezménnyel!
Részletek >>
Villa akció – golfozóknak
Akciós ajánlatunk golfozóknak: Green fee napi ár 25% kedvezménnyel!
Részletek >>
Villa akció – golfozó nyugdíjasoknak
Akciós ajánlatunk
Green fee napi ár 30% kedvezménnyel!
Részletek >>


